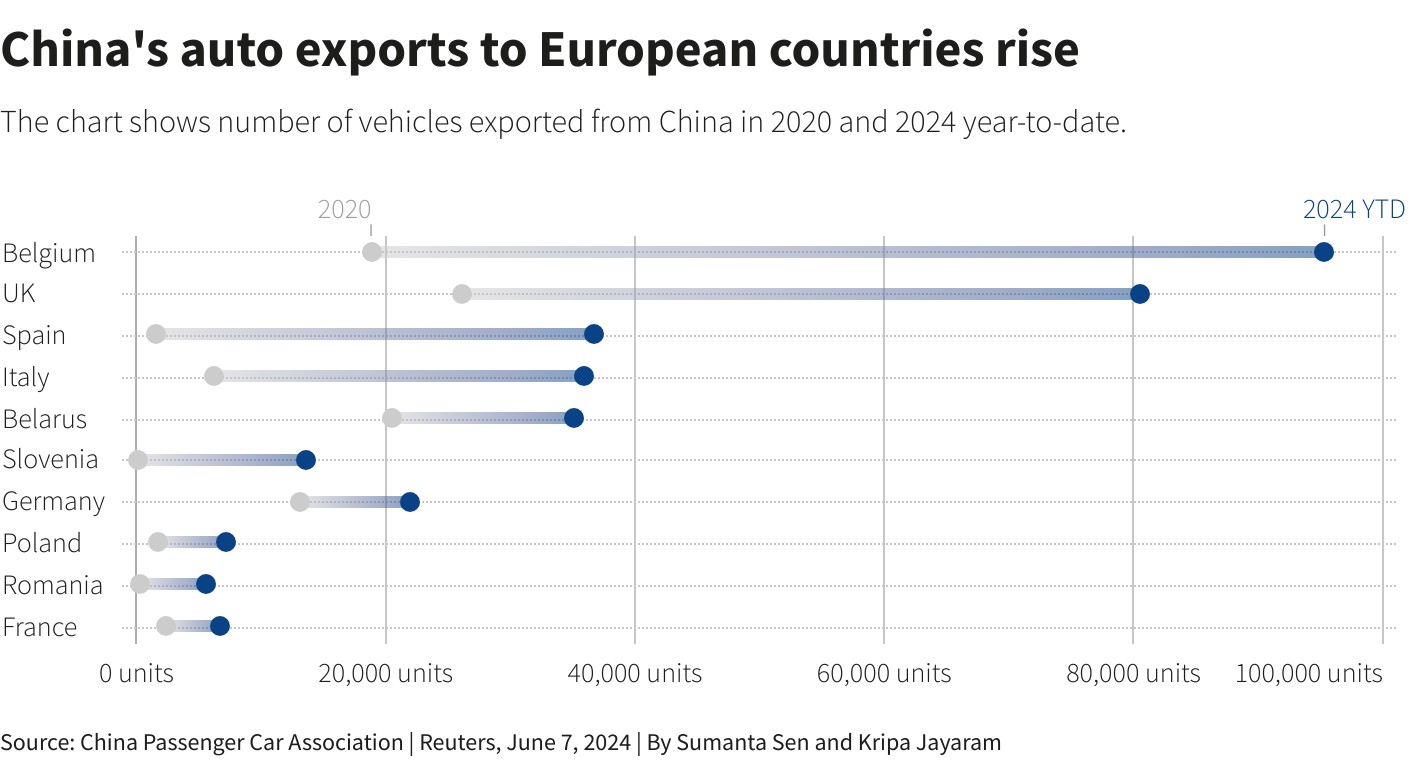
The European Union (EU) has imposed tariffs of up to 37.6% on electric vehicles (EVs) imported from China, citing unfair subsidies from the Chinese government. This move has ignited controversy within the European automotive industry, with German carmakers expressing strong opposition and the UK facing a decision of whether to follow suit.
The Impact of Tariffs
The tariffs will significantly impact Chinese EV manufacturers, particularly SAIC, the owner of MG. SAIC faces a hefty 37.6% additional tariff on top of the existing 10% import duty, a consequence of failing to cooperate with the EU's investigation. Other major Chinese EV players like BYD and Geely (owner of Volvo, Lotus, and Polestar) will also be subject to additional tariffs ranging from 17.4% to 19.9%.
The tariffs are not uniform across all Chinese manufacturers. Companies that cooperated with the EU's investigation, such as eGT New Energy Automotive (Dacia Spring) and BMW Brilliance Automotive (BMW iX3), received a slightly lower tariff of 20.8%. Conversely, those that did not cooperate, like the Spotlight Automotive joint venture between BMW and Great Wall Motor (electric Mini Cooper), face the full 37.6% penalty.
Justification for Tariffs
The EU justifies the tariffs by claiming that Chinese government subsidies distort the market and create a threat of economic harm to European EV producers. The European Commission argues that the Chinese EV value chain benefits from unfair subsidies, leading to lower production costs and artificially cheaper EVs entering the EU market. This, according to the EU, allows Chinese manufacturers to undercut European competitors and potentially hinder the growth of the European EV industry.
Opposition and Potential Repercussions
The EU's decision has been met with strong resistance from German carmakers like Mercedes-Benz, BMW, and Volkswagen Group. These companies have significant sales volumes in China and fear retaliation in the form of tariffs on their high-end gasoline-powered cars exported to China, a highly profitable market for them. China has already been targeting Germany specifically in an attempt to pressure the EU into dropping the tariffs.
The provisional tariffs will remain in place for four months while negotiations between the EU and China continue. The goal is to reach a solution compliant with World Trade Organization (WTO) regulations. However, if negotiations fail, permanent tariffs could be implemented for up to five years.
The UK's Position
The UK, which is no longer part of the EU, has not yet followed suit with the tariffs. However, the decision is likely to be a major consideration for the next UK government, particularly regarding its transportation policies. Industry experts believe that the UK will eventually have to follow the EU's lead to avoid increased pressure from Chinese manufacturers to shift their focus to the UK market for EV sales.
Unlike the EU, the UK's Trade Remedies Authority can only launch an investigation into potential subsidies for Chinese EV makers if a formal complaint is filed by a British manufacturer. As of now, no such complaint has been lodged. The Secretary of State also has the authority to initiate an investigation in "exceptional circumstances," but this option has not been exercised either.
Looking Ahead
The EU's decision to impose tariffs on Chinese EVs has created a complex situation with significant implications for the global automotive industry. The potential trade war between the EU and China could disrupt supply chains, increase consumer costs, and hinder the overall growth of the EV market. The UK's future stance on these tariffs remains uncertain, adding another layer of complexity to the situation. As negotiations progress and the UK makes its decision, the global automotive landscape will continue to evolve. These tariffs are no way as high as what the USA market plans on imposing. Currently, apart from the standard taxes that our government imposes, there is no special taxthat is imposed on Chinese electric vehicles in India.




.webp)